Strong database management facilitates fast and effective business decision-making.
Data drives everyday decision-making to help businesses complete tasks and accomplish their goals. Therefore, it requires proper management. But the question is how to effectively manage business data to ensure quick decision-making and smooth workflows? Using a database management system is the answer.
A database management system makes it easier to store, organize, and share data across your business departments. It pulls data from the various tools, platforms, and applications your business uses and centralizes its storage so it can be easily searched and retrieved. It also eliminates risks such as data loss that delay or disrupt daily workflows.
If you’re someone who works with data day in and day out or who relates to the everyday challenges of managing databases, this blog is for you. We explain what a database management system is and how you can use it to ensure data integrity and streamline data management processes.
Our lists of IT Services Agencies by location can help you find the services you’re looking for.
What is a database management system?
A database management system is a software platform that helps you store and organize data. It creates a single centralized data source that can be used by stakeholders across departments. It combines the capabilities of data manipulation, analytics, and reporting to ensure better use of key data points.
A database management system acts as an interface between your databases and employees. Employees can add, update, access, and delete data in the databases, based on the levels of permissions you assign to them. You can use database management software for:
Data management: Store, manage, categorize, and update business data.
Data retrieval: Find specific data points using the search functionality.
Queries: Run queries to perform specific actions such as calculations.
Data replication: Create duplicate instances of data and use them as a distributed database among employees.
Data security: Ensure data is secure from malicious attacks, unauthorized access, and accidents such as deleted data.
Data conversion: Transfer data from one database to another—also known as data migration.
Why do you need a database management system?
For people like you who depend on data to get their jobs done, using a database management system has multiple benefits. It assists with structured data management to ensure easy access and sharing. It also frees you from time-consuming manual processing tasks such as finding a specific data point and sharing it with employees.
In addition, database management software ensures business data is shared only with relevant internal or external stakeholders. This helps mitigate risks such as information loss or unauthorized access.
Here are a few benefits of implementing a database system into your work processes:
Increases productivity due to fewer data-related errors
Speeds up decision-making with timely and uninterrupted access to data
Improves data sharing and security by allowing access to only authorized users
Your business’s need for database management software depends on how your employees use data. For instance, some might use it for daily research (normal priority), while others might use it to develop software tools (high priority). Keep such usage scenarios in mind when deciding whether or not to use database management systems.
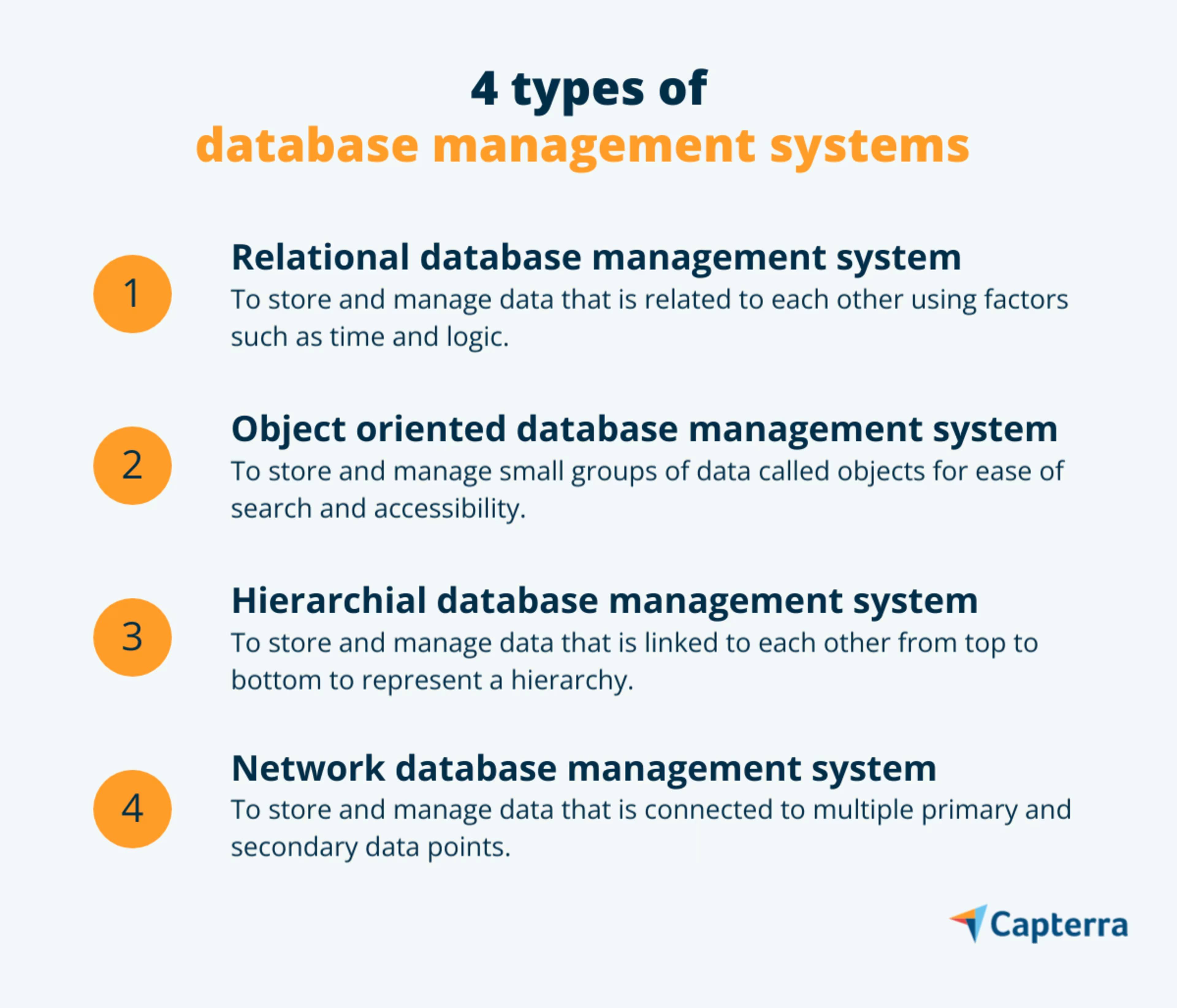
1. Relational database management system
A relational database is a collection of data that is related to each other so different data points can be combined for better usability. The related points could be time, data, or logic, and the relation can be categorized in the following ways:
One on one: A data point in one table is related to a data point in another table.
One to many: A data point in one table is related to multiple data points in another table.
Many to one: Multiple data points in one table are related to a data point in another table.
Many to many: Multiple data points in one table are related to multiple data points in another table.
A relational database management system is software that manages the storage and shareability of relational databases. It organizes data in a relational database by forming functional dependencies between multiple data points. It also stores data in an organized manner so it’s easier for employees to find and use data for their daily tasks.
A relational data structure uses structured query language (SQL) to allow employees to run queries and find the information they need. A relational database management system typically:
Stores large volumes of data
Enables fast data-fetching
Allow users to simultaneously access multiple data elements
2. Object-oriented database management system
An object-oriented database is a collection of data that is presented in the form of an object. Multiple data points are combined into a single unit or object, making it easier for employees to find and use data. This type of database is used to accomplish high-performance tasks, such as software development and programming, that require faster decision-making.
An object-oriented database management system is software that stores and manages databases as objects. It allows employees to look for complete objects instead of individual data points, resulting in a quicker search. An object-oriented database structure typically:
Maintains a direct relationship between database objects and real-world scenarios so the objects don’t lose their purpose
Provides an object identifier for employees to quickly locate objects and use them
Handles different data types such as pictures, text, and graphics
3. Hierarchical database management system
A hierarchical database is a collection of data that is organized into a tree-like structure wherein the stored data is connected through links and arranged from top to bottom. The primary data point is at the top, and the secondary data points follow in hierarchy depending on their relevance. Your business's organizational structure is a perfect example of a hierarchical database.
A hierarchical database management system is software that stores and manages hierarchical databases. It maintains accuracy in data hierarchy or flow based on the usage in work processes. Data within a hierarchical system is typically:
Easy to add and delete
Easy to search and retrieve
Follows a one-to-many relational data model
4. Network database management system
A network database is a collection of data where each data point is connected to multiple primary and secondary data points. Having interconnected data points makes this data model more flexible in terms of usage.
A network database management system is software that stores and manages the interrelated data points in a network database. This software was built to overcome the shortcomings of a hierarchical database model that doesn’t allow interconnection between data points, besides the top-to-bottom flow. A network database system typically:
Facilitates quick data access
Supports many-to-many relational database models
Allows to create and manage complex database structures
Who uses a database management system?
In the table below, we share a couple of examples of professionals who use a database management system. Please note that these are just a few examples, and there are many such professionals for whom data is on top priority to accomplish tasks.
User | Usage |
|---|---|
Application programmers | These are professionals who interact with databases to develop software apps and tools. They mostly use an object-oriented database management system to write codes and then convert them into objects for better usability. Converting large codes into smaller objects makes it less confusing for application programmers, especially when checking the performance of the developed applications. |
Data analysts | These are professionals who collect raw business data and organize it into a database. They mostly use SQL in a relational database management system to identify raw data, draw valuable insights from it, and convert the insights into action points to impact business decision-making. |
DBMS software applications are also used in the following industry functions:
Railway reservation systems: A database management system is used to manage information such as ticket bookings, train timings, and arrival/departure status.
Library management: A database management system is used in libraries to manage the list of books. This includes keeping track of issuing dates, patron names, and author names.
Banking and finance: A database management system is used to manage the list of bank transactions, mode of payments, account details, and more.
Educational institutions: A database management system is used to manage the list of students, classes, lecture timings, and the number of hours logged in by both teachers and students.
Use database management systems to enhance business decision-making
Data is key to better decision-making, and efficient database management is key to getting data right. Therefore, it’s essential to manage your business data for effective usage, accessibility, and security.
