Health information management (HIM) is a fast-growing field, with 206,300 jobs available as of 2016, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The field has a 13% growth rate per year, which is higher than the average for U.S. jobs.
High-quality HIM work is essential to “detecting health problems, defining priorities, identifying innovative solutions, and allocating resources to improve health outcomes," according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
But is HIM the right career for you?
Many people are attracted to it because you can get a job without a bachelor's degree. Plus, jobs in this space pay more than many jobs that also don't require a bachelor's degree.
To help you decide if you want to pursue a health information management career, I've researched five important aspects of working in HIM:
What HIM professionals actually do
How much education you'll need to get your first job in the field
Job titles that fall under the HIM umbrella
Tools HIM pros use regularly
How much HIM pros get paid

What do health information management technicians do?
HIM, in a nutshell, is the process of gathering, analyzing, and securing information pertinent to providing quality patient care.
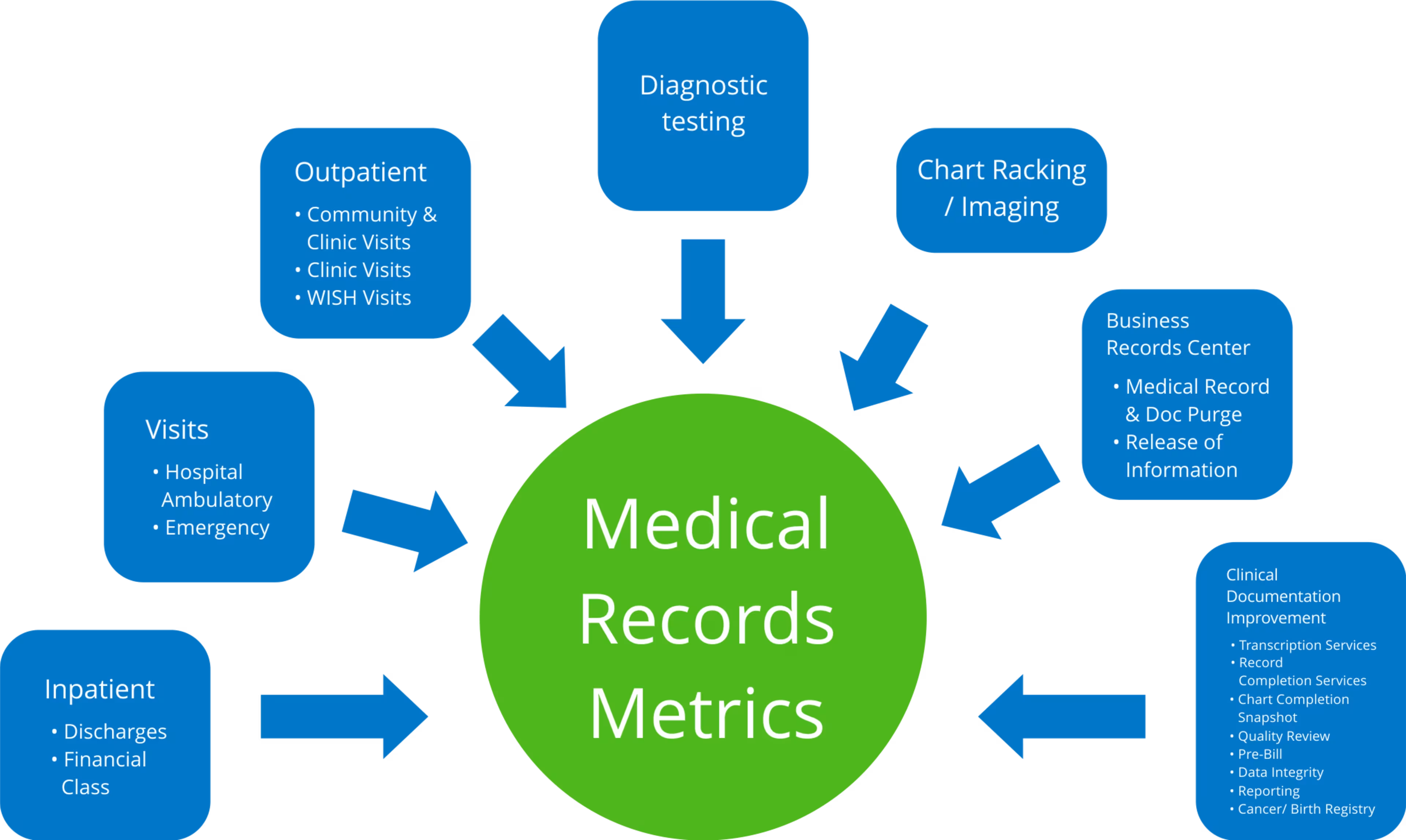
HIM data sources (__Source)
That data includes clinical, epidemiological, demographic, financial, and reference information, such as:
Patients' medical and treatment histories
Organizations' legal, professional, ethical, and administrative record-keeping requirements
Public health databases and registries
HIM tasks can include:
Collecting, storing, analyzing, and transmitting healthcare information
Ensuring the quality, accuracy, accessibility, and security of an organization's healthcare data
Creating systems for current and future healthcare data needs
Coding and categorizing patient data for insurance reimbursement
For example, HIM techs are often responsible for working with nurses and other staff to review patients' medical records to make sure they are current, complete, and accurate. They may also be responsible for tracking patient outcomes to calculate an organization's quality of care.

HIM skills needed (Source)
A sample of HIM job titles
On the Bureau of Labor Statistics website, HIM falls under the Medical Records and Health Information Technicians umbrella. Coders, registrars, and specialists are the main job titles, with the following specialties listed underneath them:
Medical coder
Medical coding specialist
Cancer registrar
Billing specialist
Certified medical coder
Registered medical coder
Outpatient surgical coder
How much education do you need to be a HIM pro?
To get a job in HIM, you need an associate's degree or certificate.
Depending on your goals, you should research degree and certificate programs in health information management, medical billing, and medical administration.
You can also get both. If you earn an associate's degree in an accredited health information management program you may also want to earn a Registered Health Information Technician (RHIT) certificate from the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). Certification shows that you're practiced and informed on medical record keeping and gives you an edge when applying for jobs.
What tools do health information management professionals use?
Depending on specific job responsibilities and how your organization chooses to allocate those tasks, a HIM pro may use the following tools:
CAC software
If you have experience using any of this software, you'll have a huge leg up when applying for jobs in this field.
How much do HIM pros get paid?
According to the BLS, 2016 median pay for a medical records and health information technician was $38,040 per year or $18.29 per hour.
PayScale has 2018 median salary data for the following job titles:
Medical coders: $17.17/hour, $39.963/year
Medical coding specialists: $17.44/hour, $41,506/year
Cancer registrars: $20.90/hour, $44,888/year
Billing specialists: $15.85/hour, $40,711/year
Certified medical coders: $17.96/hour, $40,538/year
Registered medical coders: $19.58/hour, $45,950/year
Outpatient surgical coders: $21.46/hour, $41,766/year
Keep in mind that location has a huge impact on salary. To estimate what you'll make, use PayScale to look up the job title and set your location to see the most accurate averages.

States looking for health IT talent (Source)
Where is the field headed?
Data analysis, data visualization, and cybersecurity are three skills healthcare organizations will prioritize in future hiring decisions.
Darren Dworkin, chief information officer of Cedars-Sinai Health System in Los Angeles, told U.S. News that the three skills that will make young people competitive in the healthcare industry are: "data, data, data."
The U.S. has generated obscene amounts of healthcare data in recent years, and mining it for insights and predictions holds tremendous potential value. "There are unbelievable opportunities in the pure data science world," Dworkin said.
Is HIM the field for you?
HIM is a fast-growing, well-paid, high-tech job that doesn't require all that much education to get started in.
But is it for you? Let me know what you think in the comments, and also check out the following medical career posts for more tips and information:
How Much Do Doctors Make in 2018?