Several human roles will likely disappear from restaurants in the near future.
Cutting-edge automation technology like robotic chefs and fully autonomous kitchens have picked up steam in the media. Do restaurant leaders share Silicon Valley’s dream of robotic employees as the silver bullet for the hospitality industry’s hiring and efficiency woes?
In our new study of restaurant owners, managers, and executive chefs who currently use automation tools in their restaurants, we found that the majority believe hosts, baristas, and drive-through operators can be easily replaced by today’s automation technology.
While chefs, managerial staff, and waitstaff appear safe for now, automation is likely to replace quite a few human roles in the coming years. We'll look at the top restaurant technologies outperforming human employees today.
key insights
Automation already has mass appeal: Three-quarters of restaurants surveyed are currently using automation in three or more areas of operation.
Front-of-house roles are ripe for automation: More than half of restaurant leaders say drive-through operators, baristas, hosts, and cashiers can be easily automated with today’s technology.
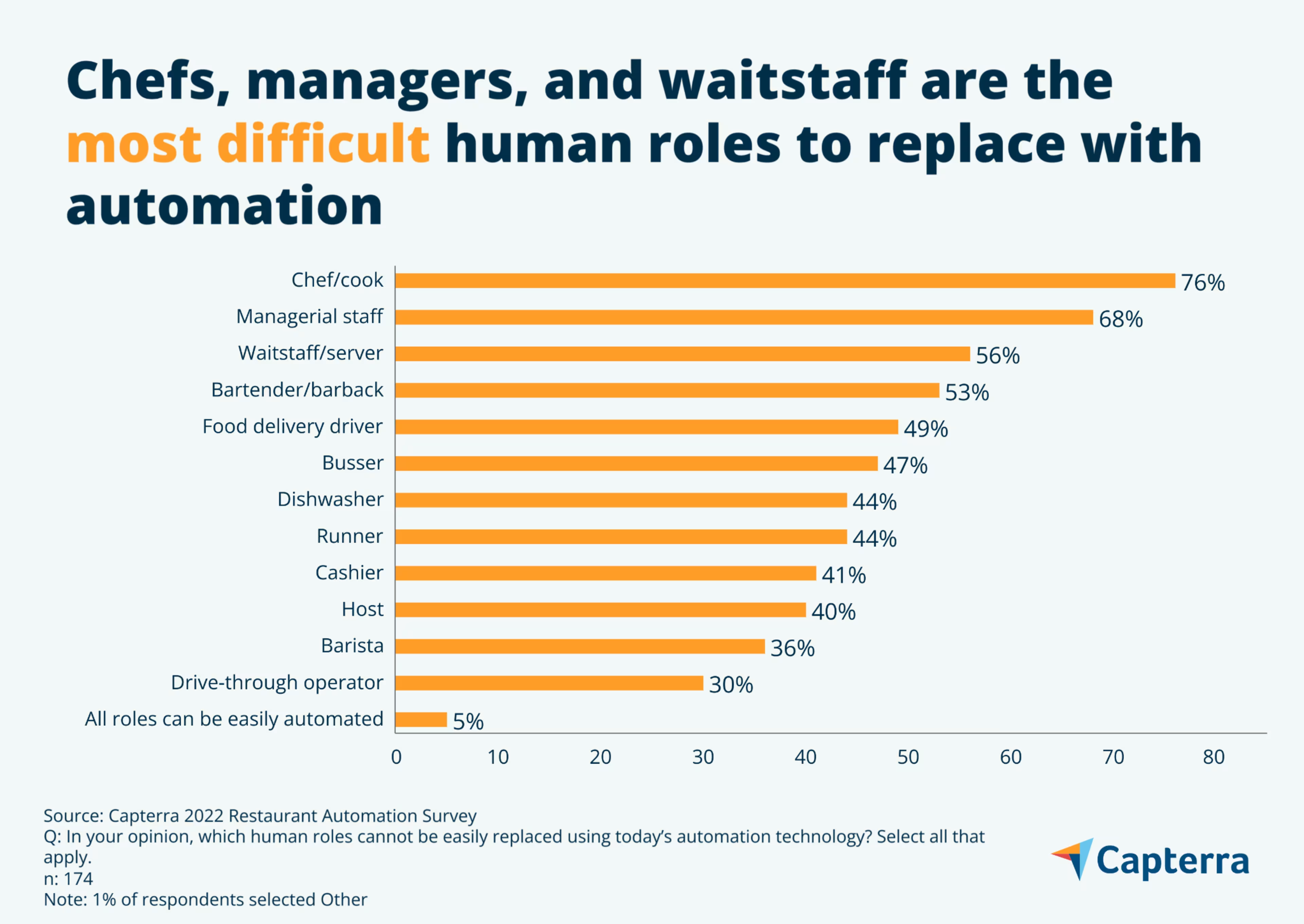
Chefs are currently the safest restaurant role: 76% of restaurant leaders say the role of chef/cook cannot be easily automated with today’s technology.
Managers matter more at chains: 75% of leaders at chain or franchise restaurants say managerial staff cannot be easily replaced with automation, versus just 58% of independent restaurant leaders who say the same.
Restaurant leaders agree on several easily automatable roles
Several front-line restaurant roles may be on the chopping block in the future—restaurant leaders believe that hosts, baristas, and drive-through operators can be easily automated with today’s technology.
Leaders also agree on a few irreplaceable human employees—most say chefs and cooks are the least-automatable jobs, followed by managers, waitstaff, and bartenders. This includes 76% of managers of fast-food restaurants, whose kitchen staff are firmly in the crosshairs of cutting-edge food service robotics developers like Miso Robotics, which has created robots that can mix beverages and work deep fryers all on their own.
Breaking down the results based on restaurant type reveals some interesting similarities. Let’s examine which roles are ready for automation, according to leaders at table service and quick service restaurants.
Table service versus quick service restaurants
Leaders from both restaurant types agree that human baristas and drive-through operators are on their way out.

Additionally, more than half of table service restaurant leaders say hosts are replaceable. On the quick service side, 61% of leaders believe dishwashers can be automated with existing tech.
Both groups are less decisive on food delivery drivers: 50% of table service managers and 49% of quick service managers feel the role is not easily automated. This is good news for in-house delivery staff, as well as the many former restaurant employees who recently shifted to gig work for DoorDash or UberEats—companies that offer comparable pay with a level of workday flexibility most restaurants don’t.
The fact that both table service and quick service restaurants rank managers as the second-safest role may be due, in part, to the fact that most of the respondents are managers themselves. A point of interest emerges in examining “mom and pop” restaurants versus those that belong to a chain, franchise, or restaurant group.
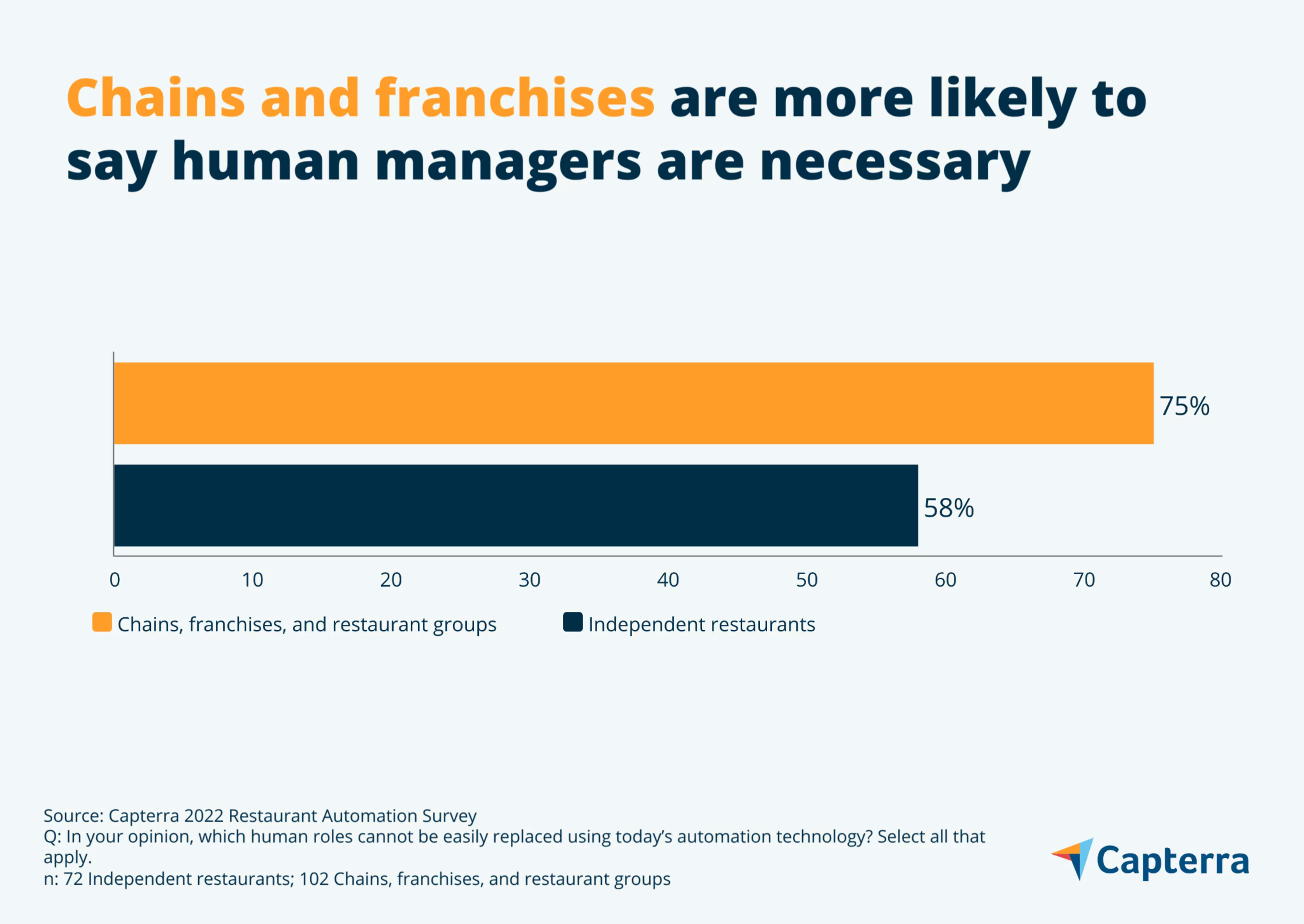
Managerial staff came in as the number-one least-replaceable role for chains, franchises, and restaurant groups, but ranked fourth for independent restaurants, trailing chefs, waitstaff, and bartenders.
This reflects a cultural difference between independent restaurants and chains or franchises— independent restaurants place more emphasis on the human touch as administered by empowered chefs and skilled, attentive front-of-house staff, whereas chains or franchises value a management hierarchy that can maintain established workflows and consistency across many restaurant locations.
It also reveals a model for how restaurants could reorganize their rosters to better allocate the human touch while leveraging automation’s efficiency and speed. More on that later.
76% of restaurants currently use 3 or more automated tools
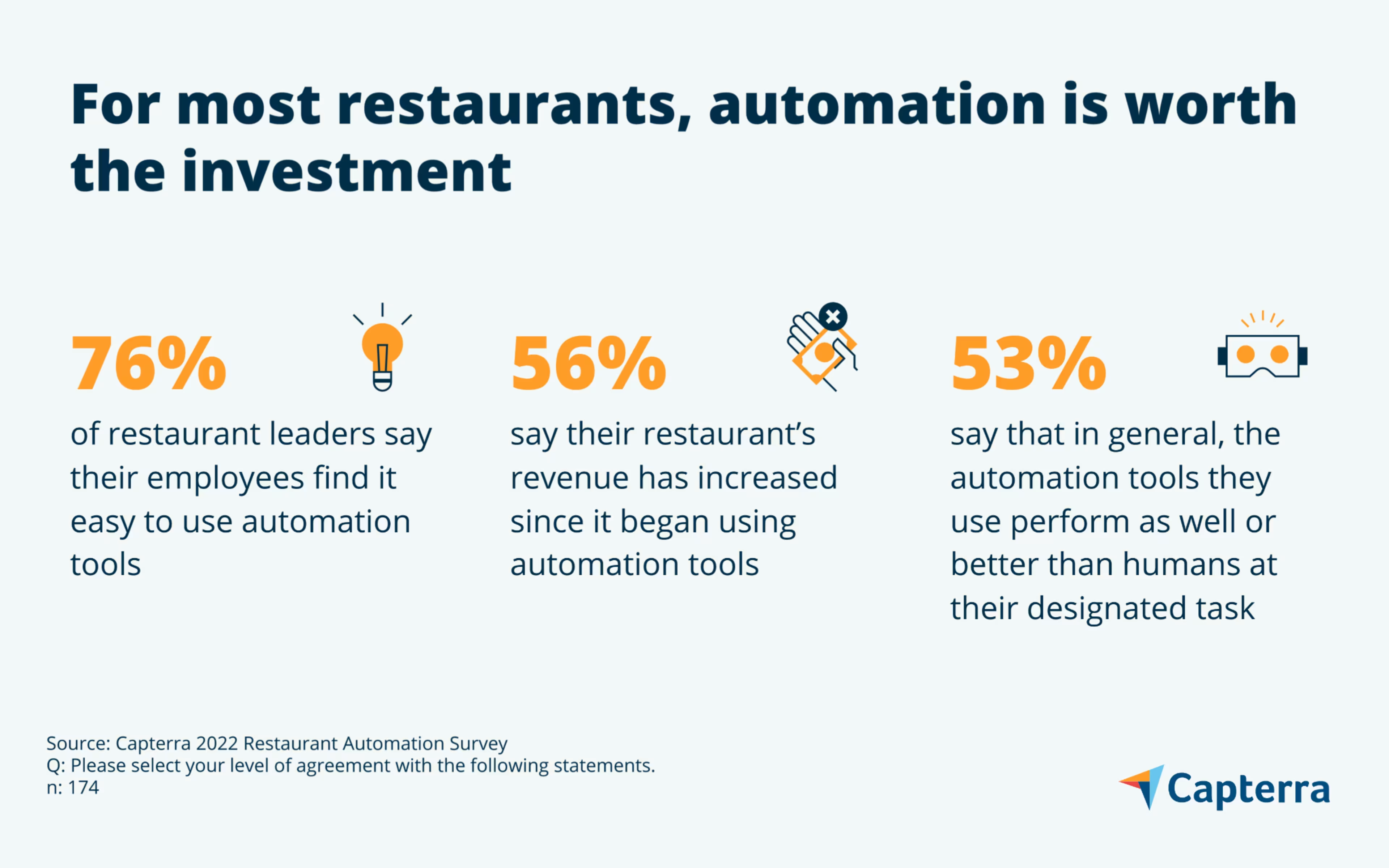
Restaurant leaders are embracing automation technology across the board. Three in four leaders surveyed say their restaurants have adopted automated solutions in at least three different areas of operation, and most say it’s working out pretty well.
For starters, over three-quarters of leaders say their employees find it easy to use their restaurant’s automation tools. Over half say revenue has increased since implementing the tools. For restaurant owners looking to invest in automation, those are great selling points.
Where restaurants apply automation depends on service type, though overall most focus on automating behind-the-scenes work.
Nearly all restaurants today (96%), both table service and quick service, use automation tools in their back-of-house operations. This includes day-to-day kitchen functions such as inventory management, food prep, food safety monitoring, and order capacity, as well as administrative areas such as employee management and performance analytics.
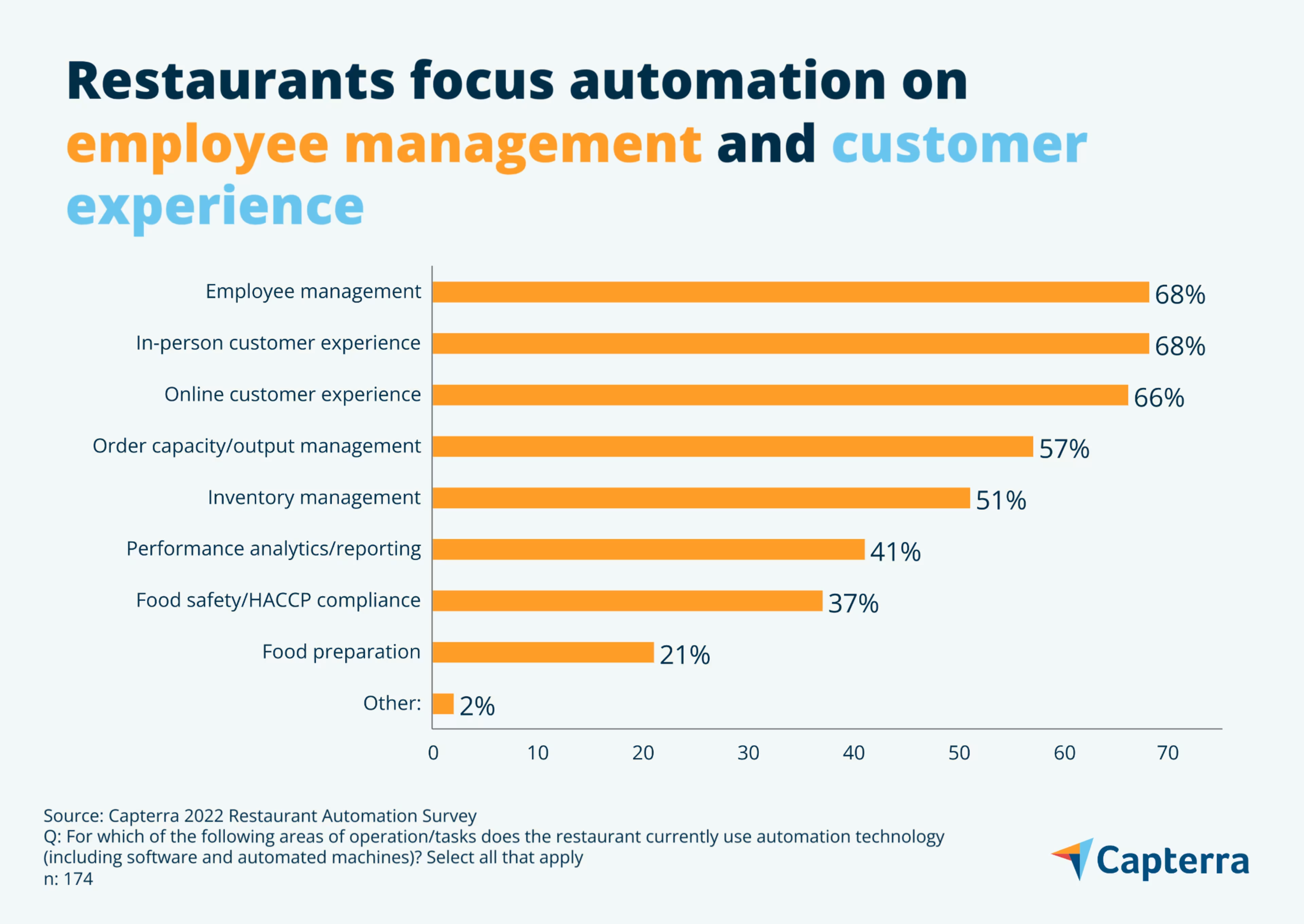
Front-of-house tools are also popular with both groups. Front-of-house automation can include the on-premise dining solutions that soared in popularity during the pandemic, such as QR code menus and contactless payment options. It also encompasses mobile ordering apps, digital loyalty programs, and online reservation software.
How to find the right automation solutions for your restaurant
Our research shows that while not all human roles are ready to be replaced by robots just yet, restaurants can go ahead and introduce automation in a few key areas. Strategically incorporating automation could alleviate the labor crisis currently plaguing the restaurant industry.
One trend in this study offers clues to where to start with automation: Restaurant leaders are prioritizing the human touch for roles directly involved in the flow of prepared food to customers, while implementing automation for more peripheral roles.
Automation doesn’t have to fully replace humans—it can also be used to lighten the loads of the humans that remain employed. Leaders struggling to keep roles filled should keep in mind that repetitive, boring work is a roster killer in the restaurant industry. Using automation to reduce the amount of time employees spend on menial tasks can help make restaurant jobs more creative and fulfilling while introducing efficiencies to make operations run smoother overall.
Here’s a framework for how table service and quick service restaurants should approach further automation:
Table service restaurants:
Allow human kitchen staff and waitstaff to shine creatively and provide the human touch to customer experience.
Automate repetitive tasks and roles not directly related to food preparation or delivery.
Quick service restaurants:
Employ more human managers to oversee and troubleshoot automated work performed by software and machines.
Provide the human touch as needed for a fast-paced but personable customer experience.
Take the following steps to make sure you choose the right mix of automation tools to suit your restaurant.
Support your restaurant’s service type
As we’ve seen, table service and quick service restaurants approach automation and human resources differently. Before adding automation tools to the mix, restaurants should identify where the human touch is most needed in their environment and ensure those areas are staffed with human employees.
For table service, prioritize chefs or cooks, bartendenders and barbacks, and waitstaff.
For quick service, focus on kitchen staff, cashiers, and delivery drivers.
Then, look for tools to reduce the repetitive workload for these employees and further support or replace peripheral roles.
Consider employees' pain points
Part of your research should involve talking to employees about their work. Identify their most repetitive tasks, and invest in software or devices that can execute them automatically. That way, employees have more time to tend to customers and food quality.
Here are some ideas:
Switch from call-in reservations to online reservation booking software so hosts and waitstaff can spend more time enriching the dine-in customer experience.
Use a digital kitchen display system to cut out the fuss of handwritten or printed order slips, so kitchen staff can keep their workspaces neater and focus on preparing high-quality, well-plated dishes.
Payroll software can eliminate the headache of calculating employee tips and helps ensure employees get paid on time.
Use a performance analysis tool to determine which weekly shifts see the most traffic and sales, so you can schedule employees to support high-volume hours.
Add online ordering to your restaurant’s website so waitstaff don't have to spend time on the phone collecting takeout orders.
Do research to find the tools that work best for your restaurant
Restaurants tend to stick with the first automation tools they try. Whether due to budget constraints, limited time to find alternatives, or simply because their tools work well right away, just 21% of surveyed restaurant leaders have stopped using an automation tool they previously used. Typically, this was because the tool was difficult for employees or customers to use, or did not perform as advertised.
Be sure to do plenty of research to compare your options before you go all-in on one solution. There are a variety of tools available that do similar things, but some are better suited to specific kinds of restaurants.
Automation tools can help your restaurant operate more efficiently and improve employee retention by increasing creative opportunities for human staff. By adopting the tools that best support your service model, you can help protect your restaurant from today’s labor shortage while investing in future-focused solutions.
