Master data management is a game changer when it comes to data processing and analysis. Learn all about it here.
According to Gartner’s Hype Cycle, master data management is two to five years away from reaching a stable and consistent level of use for higher education institutions (full content available to Gartner clients). If your small business hasn’t yet embraced this technology-enabled initiative, you’ll want to make plans to get on board soon.
If you’re new to master data management, or MDM, this guide is designed to get you up to speed.
What is master data management?
Master data management refers to the network of people, processes, and technology that work together to maintain a company’s master data assets and ensure that they’re consistent, accurate, and secure. A master data asset, also known as a master data entity, can be defined as any customer, employee, vendor, supplier, account, product, or site in a business transaction. Put simply, it’s any person, place, or object involved in the operation of your organization.
MDM is important because it gives organizations the ability to make informed decisions that are backed by updated, organized data and analytics. It also prevents data silos where certain data is accessible to just one group in an organization.
While MDM is concerned with the processes of data management, data governance is concerned with the rights and rules of those processes: Who can do what with the data, when and where. And while we’ll see this term more later on, it’s important to know that data governance ensures that data responsibilities are assigned to the appropriate people.
Master data management software serves as a central repository for enterprise data that is collected from multiple systems. It uses machine learning to clean, verify, and organize that data in a way that helps ensure data quality as well as to link dispersed data points together so that your organization can trust in a single source of master data.
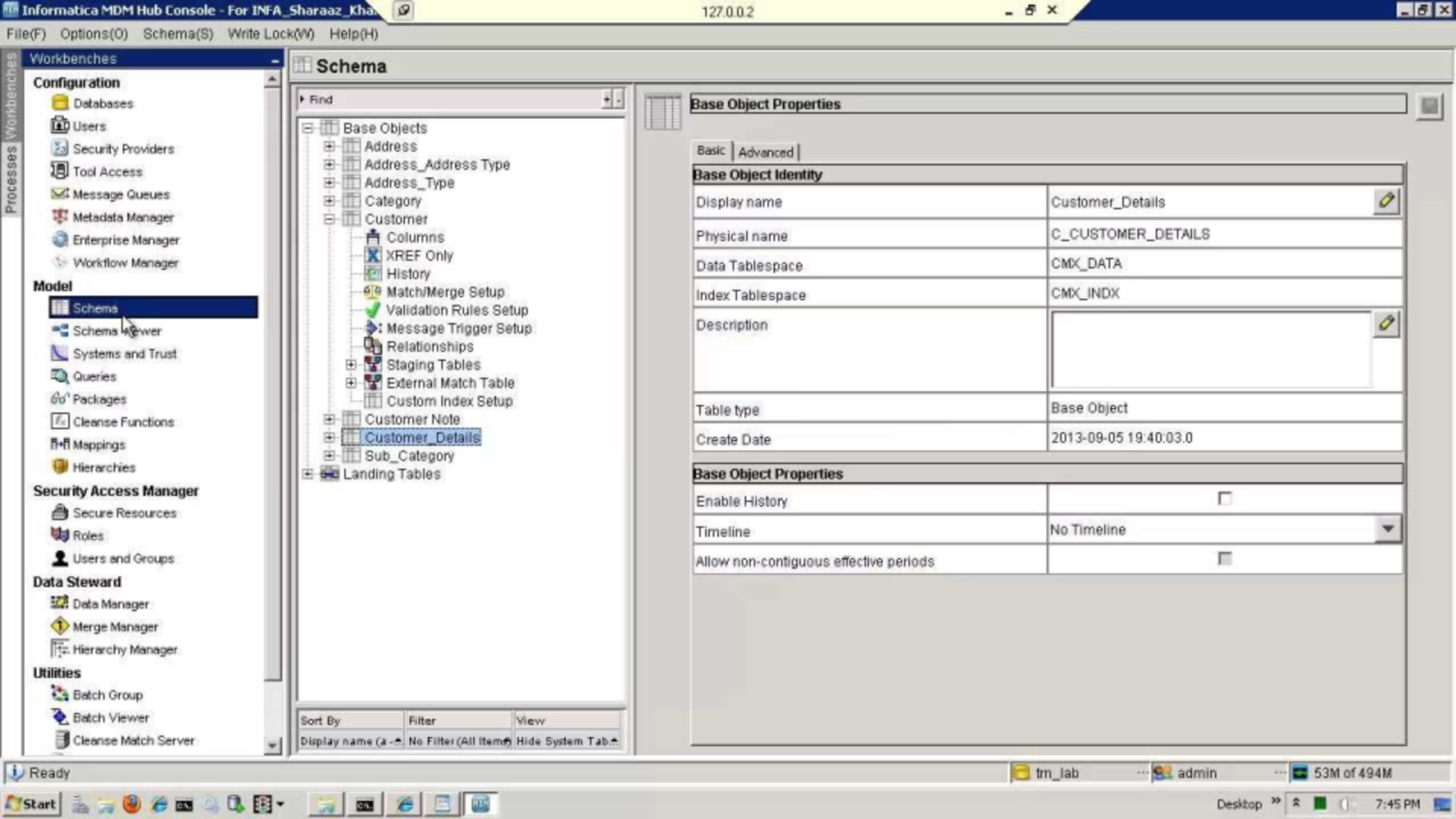
Dashboard for Informatica MDM (Source)
Common MDM software features include:
Data masking, which protects sensitive data.
Hierarchy management, which organizes data into tiers (i.e., team, department, national headquarters, global headquarters).
Relationship mapping, which tracks associations between data assets.
Workflow visualization, which allows users to see a series of projects and tasks as well as their assignees and stages of completion.
A few MDM vendors offer free versions of their platforms, but free trials are more standard.
Investing in MDM software can lead to more transparency, greater operational efficiency, improved customer experience, and sustainable company growth. Next we’ll discuss how your small business can leverage master data management.
Find providers that can help with your business needs by using our lists of managed service providers agencies by location.
How can SMBs leverage master data management?
While master data management stacks are typically better suited for larger enterprises, SMBs can look to platforms that allow application building. This way, you can start by adopting a small set of features, such as data profiling, and then upgrade when you’re ready.
SMBs can build a foundation for a successful MDM program by:
Signing up for a trial of a master data management platform to learn how you might implement different features such as data cleansing or profiling.
Clearly defining the business outcomes you want to achieve from any master data management tool you plan to adopt.
Master data management can be a game changer for small business owners when it comes to the ways they collect, organize, process, and analyze data, but you’ll want to be sure to engage with stakeholders early on, otherwise you will struggle to meet expectations of value.
Areas that benefit from master data management
Your organization would especially benefit from an MDM solution if it deals with big data. Big data refers to high volumes of data assets that call for more advanced methods of processing and analysis.
Whether your data assets include student records, medical records, product inventory, or customer data, master data management can keep your files organized, uniform, and safe.
To give you a better idea of what master data management looks like in action, here are some examples of areas that benefit from implementing an MDM tool.
Higher education
Colleges and universities rely on a network of offices and departments to process and maintain information. This includes registration, schedules, transcripts, grades, tuition payments, and other student fees. There are also scholarships, meal plans, housing arrangements, and athletic aid agreements. There’s a lot to keep track of, and this is just the student side of the data.
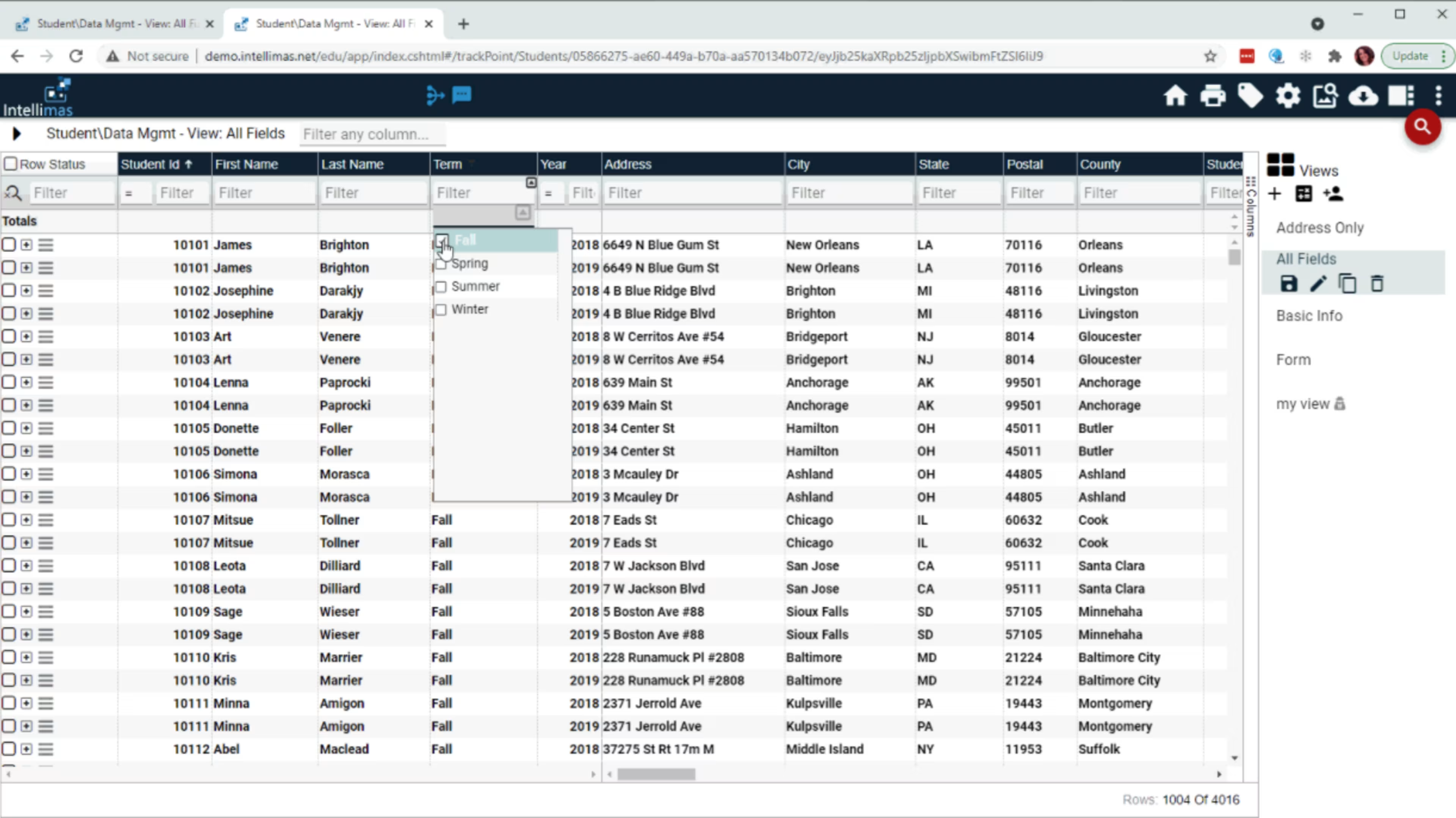
Screenshot of student data management feature from Intellimas, taken by author (Source)
If you’ve ever attended or been employed at a college or university, you know that a lot of these record-keeping systems can be antiquated. MDM gives higher education a way to merge the myriad of systems in use so that this data can be more easily accessed by those who need it:
Faculty and student data can be combined for easier course scheduling.
Faculty and advisors can be alerted when a student’s grades or attendance drops, aiding in retention efforts.
MDM can assist facilities management in the maintenance of physical assets such as computers, shuttle buses, or even washing machines in dorms to prevent interruptions to resources that students depend on for their success.
Key takeaway
The goal of using MDM in higher education is to improve student record keeping and increase transparency by providing a more holistic view of all aspects of their college experience.
Customer relationship management
According to Gartner, the success of any customer relationship management (CRM) program depends on master data management (full content available to Gartner clients). That’s because it’s nearly impossible to address and respond to the variety of customer needs without a well-maintained, single source of customer data.
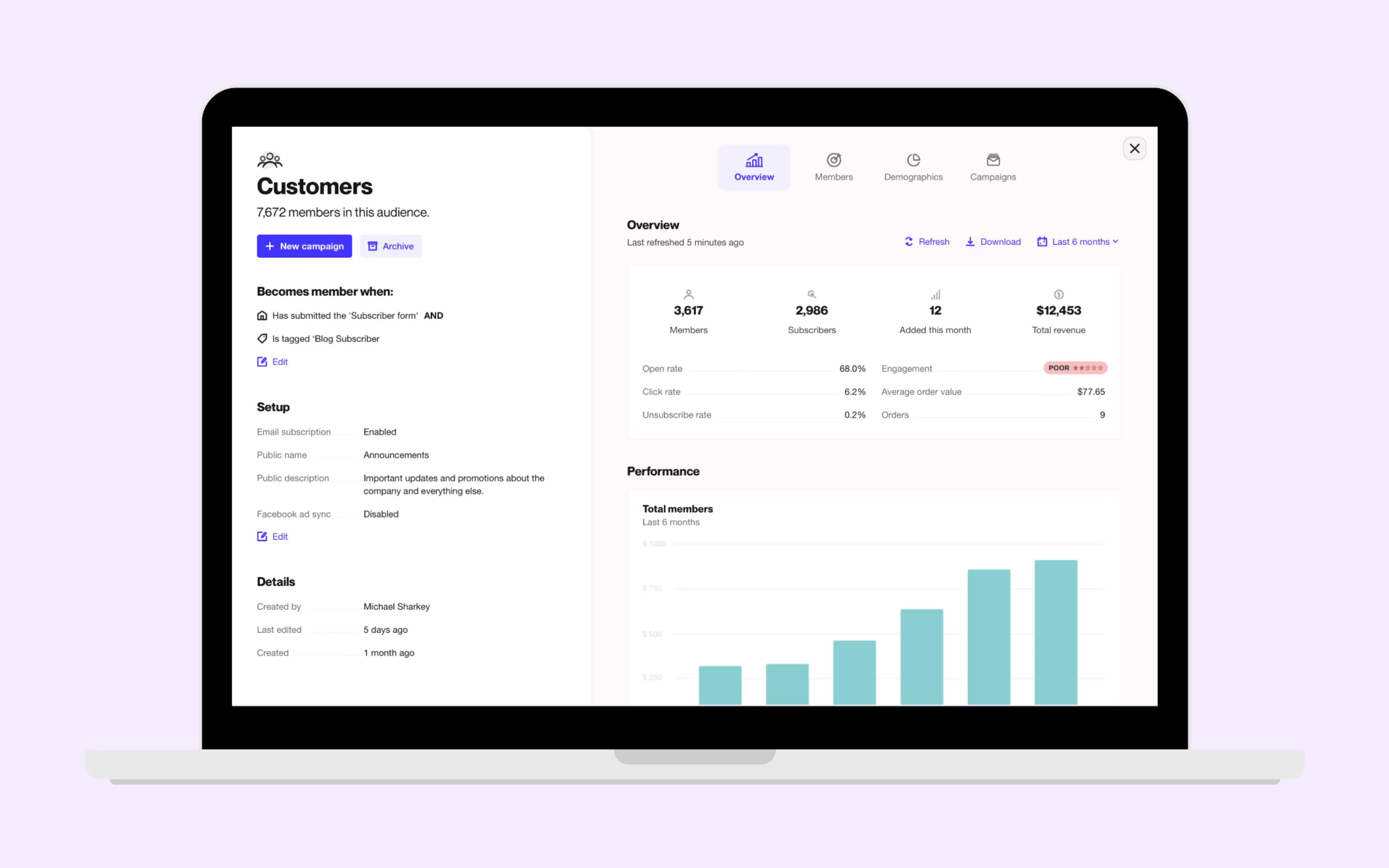
Audience segmentation feature on Autopilot (Source)
MDM can help boost customer engagement and satisfaction in the following ways:
Ensuring that all customer communications are timely and relevant by maintaining an accurate, in-depth knowledge of their purchase history and patterns.
Preventing representatives from contacting customers multiple times about the same issue.
Granting all departments (i.e., marketing, sales) the same access to customer data.
Key takeaway
The goal of using master data management in CRM is to ensure that the entire organization has a 360-degree view of their customers, resulting in a more consistent customer experience.
Healthcare
Healthcare is another area where the accuracy, consistency, and security of data are extremely important. Data assets in healthcare include patients, providers, practices, insurance plans, prescriptions, and more.
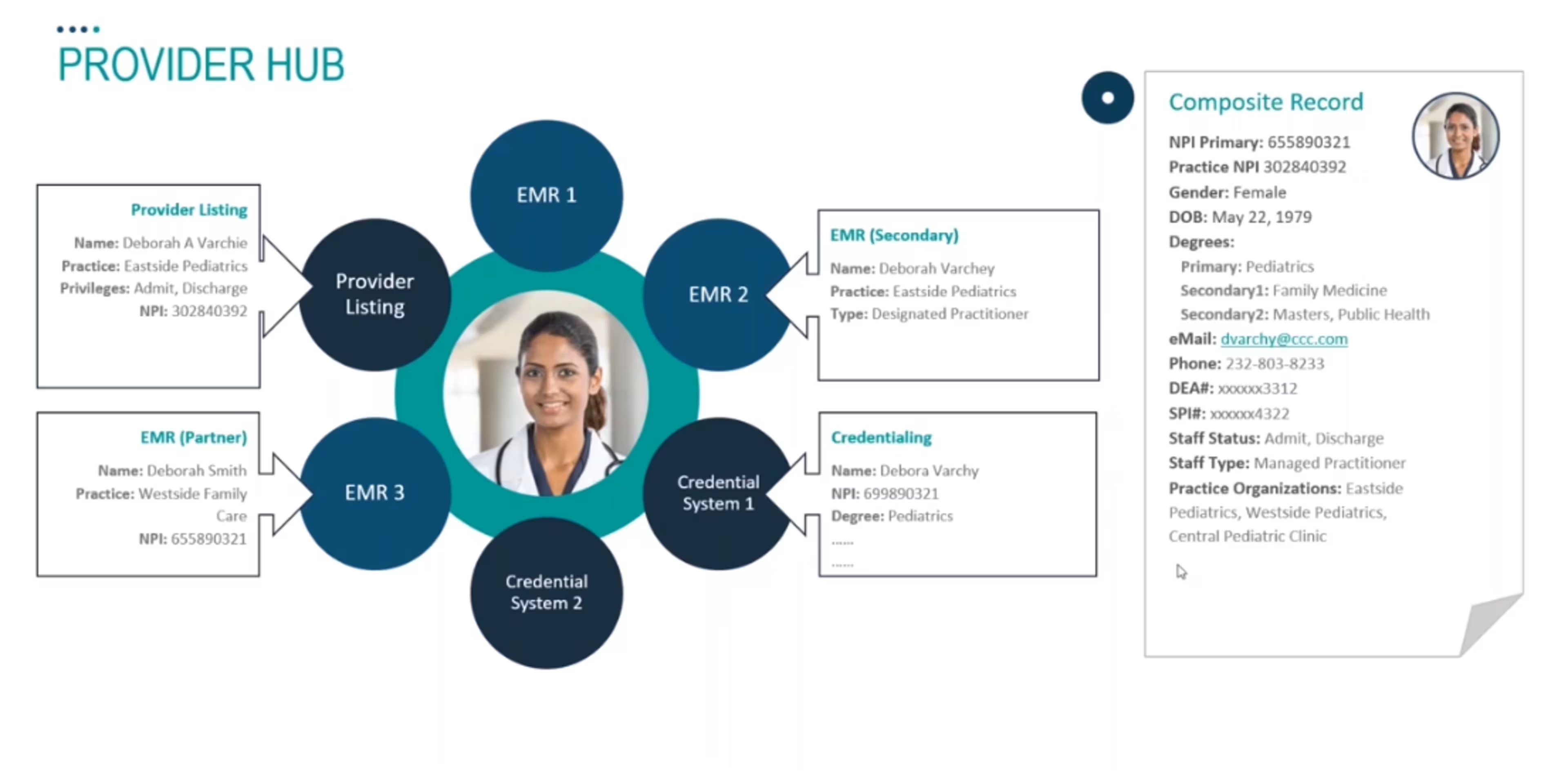
Screenshot from MDM platform Profisee, taken by author (Source)
Because of patient confidentiality laws, data governance and stewards are particularly critical when it comes to the use of master data management in healthcare.
Healthcare providers can benefit from MDM in the following ways:
Better coordinated care among multiple providers, with all physician notes, lab tests, and results for a patient in one place.
A more streamlined transfer of information from physicians to insurance providers.
Smoother onboarding for new employees.
Key takeaway
The goal of using master data management in healthcare is to ensure the security of sensitive data and to improve communication among patients, physicians, and staff.
A list of software systems that support master data management
Master data management is usually less of a feature and more of a method that platforms that already exist use to help companies collect and organize their data. However, data management can be offered as a standalone feature of platforms that cater to the needs of more specific markets, such as the ones we discussed in the previous section. If you’re interested in software solutions that are built with your specific industry in mind, check out the following software systems.
Student information system software
Student information system (SIS) software helps educational institutions automate assignment distribution, grading, and other communications with students and their parents. This software also serves as a repository of documents related to students’ tenure at an institution.
CRM software
CRM software enables customer interaction, support, and relationship management. It keeps all contact information in one place, tracks customer communications, and integrates with email services, among other features.
Electronic medical records software
Electronic medical records (EMR) software allows medical practices and healthcare facilities to record, organize, and manage patients’ medical records. EMRs are the digital imprints of prescriptions, charts, and the complete treatment details of patients. This software uses industry-approved codes for recording and streamlining data entry.
EMR software helps practitioners upgrade from the traditional pen-and-paper approach to an electronic recording system. It even helps them enroll for Meaningful-Use (MU) incentives offered by the United States government.
EMR software is closely related to electronic health records (EHR) software and is often sold as an integral part of the practice management software suite.
Alternatives to use instead of master data management
While the benefits of master data management are numerous when implemented strategically, it can still be labor-intensive and costly, particularly for SMBs. And in many cases, the data owner might not agree with rules set by your data governance team, as data strategist Eric Mack points out.
If your business is not quite ready for MDM, here are a couple of alternatives:
Manual data entry: Many organizations have an administrator whose primary responsibility is manual data entry. While it’s tedious and prone to human error, it works for small business owners on a budget. For organized data entry that’s easy to access and share, opt for a cloud-based spreadsheet application, such as Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel.
Forms automation software: A step up from manual data entry is forms automation software, which automates the processing of documents electronically. If you work in healthcare, you can use these tools to collect patient and visitor information. If you work in HR, you can use it to collect employee feedback. Retailers can use it to create invoices and organize product data, and customer service teams can use it to generate support tickets. It won’t clean and merge your data in the same way as master data management software, but it’ll save you and your team time on data entry and allow you to access your data in an easy-to-read format.
Want help finding master data management software?
Check out our list of master data management software systems. Filter by features or cost, compare different software options, and read hundreds of reviews from business owners just like you to find the best fit for your needs.
Note: The applications mentioned in this article are examples to show a feature in context and are not intended as endorsements or recommendations. They have been obtained from sources believed to be reliable at the time of publication.
